Summary of recent research progress in the field of liver diseases
April 27, 2018 Source: WuXi PharmaTech
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];1. Two new drugs bring hope to patients with primary biliary cholangitis
Recently, preliminary results from two ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials have shown that new tropifexor and seladelpar may be active in patients with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) who are not responding to current standard care. Efficacy, safety and tolerability characteristics.
Primary biliary cholangitis is a progressive cholestatic liver disease characterized by immune-mediated intrahepatic bile duct injury. For many years, the main treatment for PBC was ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), but up to 40% of patients treated with UDCA developed persistent alkaline phosphatase (ALP) or elevated bilirubin, in addition to 3-5% of patients cannot tolerate treatment. These patients need new therapies to improve their condition.
An ongoing phase 2 clinical trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of tropifexor in patients with PBC. Tropifexor is a novel selective non-bile acid Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist that has been shown in preclinical animal studies to reduce cholestasis and hepatocyte damage. The trial enrolled PBC patients who underreacted to UDCA who were randomized to receive Tropifex 30 micrograms, 60 micrograms, 90 micrograms or placebo, once daily for four weeks. The primary endpoint of this trial was the change in gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) from baseline. The data showed that GGT, ALP, bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) showed a dose-dependent decrease in patients receiving tropifexor on day 28, at 90 μg In the tropifexor group, GGT was reduced by 72% and ALT was reduced by 41% (p < 0.001 compared with placebo). Also, tropifexor is generally safe and well tolerated at the test dose. <>
Another phase 2 clinical study evaluated the efficacy and safety of selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta (PPAR-delta) seladelpar in patients with PBC. PBC patients who were underreactive or intolerant to UDCA were randomized to receive three doses of seladelpar (2 mg, 5 mg or 10 mg per day). The primary endpoint was the change in ALP from baseline. At 12 weeks, the ALP changes for the 2 mg group (n=6), the 5 mg group (n=25), and the 10 mg group (n=22) were -21%, -33%, and -45%, respectively. At 26 weeks, 29% of patients had normal ALP. Also, seladelpar was generally well tolerated and no aminotransferase safety signal was observed.
2. Combination of drugs for NASH has achieved promising clinical results
Gilead has released data from a proof-of-concept study for patients with advanced fibrosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) who have been evaluated for the use of apoptotic signaling regulator 1 (ASK1) inhibitor selonsertib in combination with acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase (ACC) inhibitor GS-0976, or the effect of a selective non-steroidal Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist GS-9674.
NASH is a serious non-alcoholic fatty liver disease characterized by accumulation of liver fat, accompanied by inflammation and cellular damage. Inflammation can lead to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, portal hypertension, liver cancer, and ultimately liver failure. However, there are currently no approved treatments for NASH.
The study included 70 patients with NASH who were diagnosed with NASH and liver fibrosis stages F2 to F3 based on tissue biopsy or magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) and MRI proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF). They received selonsertib 18mg plus GS-0976 20mg (n=20), or selonsertib 18mg plus GS-9674 30mg (n=20), or only monotherapy (n=10 per group), once daily for 12 weeks . The results showed that the largest change observed after 12 weeks of treatment was a decrease in liver fat content, which occurred in the regimen using GS-0976. Improvements in liver biochemistry and/or fibrosis markers compared to baseline were also observed in the two co-administered groups. In patients treated with selonsertib plus GS-0976, the kinetic markers showed the greatest reduction in the rate of synthesis of the fibrosis marker lumican. There was a similar incidence of adverse events between patients treated with monotherapy and combination therapy. No patients stopped treatment too early.
“Gilead is focused on addressing the most serious unmet needs of NASH patients, those who require advanced fibrosis,†said Dr. Norbert Bischofberger, vice president and chief scientific officer of Gilead Research and Development. “We are unique in our research. Drug-linked therapy with a potential complementary mechanism. The initial data provided this time is an important advancement in our goal to improve the prognosis of patients with advanced NASH fibrosis."
3. Is it expected to overcome chronic hepatitis B? RNAi therapy significantly reduces hepatitis B surface antigen
A few days ago, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals released clinical trials of RNAi therapy ARC-520 for the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The data suggest that ARC-520, in combination with standard therapy for hepatitis B, can significantly reduce and chronically suppress hepatitis B surface antigen levels (HBsAg) in patients.
Chronic hepatitis B virus infection is the most common severe liver infection in the world, with 400 million patients worldwide. Hepatitis B may cause cirrhosis and liver cancer, which is the cause of 80% of primary liver cancer. Current standard therapies for chronic hepatitis B are oral nucleotide/nucleoside analogs (NUCs) or interferon injections. But patients need to take their medicines for life.
Arrowhead's ARC-520 therapy is an innovative treatment for chronic hepatitis B using RNAi technology. ARC-520 is capable of targeting mRNA produced by covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) formed by HBV in hepatocytes, thereby degrading viral mRNA and reducing the possibility of viral replication.
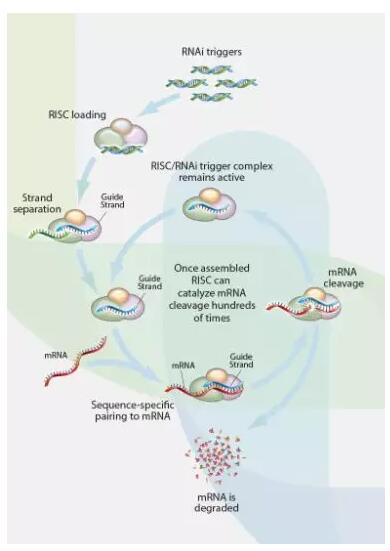
RNAi refers to a natural cellular mechanism by which short oligonucleotide molecules called RNAi trigger silent gene expression and regulate protein production. (Source: Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals official website)
The data presented this time came from a multi-dose extended clinical trial called Heparc-2001. In this study, 8 patients with chronic hepatitis B (5 HBeAg-negative, 3 HBeAg-positive) received a standard dose of 4 mg/kg body weight of ARC every 4 weeks while receiving standard therapy entecavir (ETV) daily. 520 injections. Some patients received up to 9 ARC-520 treatments. The patient continued to use ETV after receiving the last ARC-520 treatment. Researchers regularly check the levels of hepatitis B virus DNA, RNA and antigen in their bodies. After the ARC-520 treatment was stopped, these parameters were followed for 12 months.
The results showed that ARC-520 therapy completely eliminated HBsAg in the blood in a HBeAg-negative patient. One ARC-520 treatment combined with ETV can maintain the effect of reducing HBsAg for 44 weeks, and multiple ARC-520 treatments can be further reduced. HBsAg levels were able to reduce HBsAg levels by up to 5.3 log10. ARC-520 therapy stimulated a sustained host immune response in two HBeAg-positive and two HBeAg-negative patients, which resulted in a mild increase in ALT levels. The side effects caused by ARC-520 therapy in patients are mild side effects.
The key to curing chronic hepatitis B is to trigger a sustained host response, and the results of this trial suggest that ARC-520 therapy can still maintain HBV efficacy after treatment is terminated, which means that ARC-520 therapy based on RNAi technology can stimulate persistence. Sexually beneficial to control the host response of HBV.
4. NASH new drug has made important progress, ending phase 2 clinically
MediciNova Biopharmaceuticals recently announced that MN-001 (tipelukast) is a non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with hypertriglyceridemia (NAFLD) due to important positive results in the interim analysis. Phase 2 clinical trials were terminated early.
NASH is a severe nonalcoholic fatty liver disease characterized by accumulation of liver fat, accompanied by inflammation and cellular damage. Inflammation can lead to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and liver cancer, and ultimately to liver failure. NASH is an emerging health crisis that affects 3% to 5% of the US population and 2% to 4% of the global population, which is responsible for the rapid growth of liver cancer and liver transplantation in the United States.
MN-001 (tipelukast) is a novel oral bioavailable small molecule compound that produces anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic activities in preclinical models through several mechanisms, including leukotriene (LT) receptor antagonism, Phosphodiesterase (PDE) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) inhibition. The inhibition of 5-LO by MN-001 and the 5-LO/LT pathway are considered to be new approaches to the treatment of fibrosis. MN-001 can down-regulate the expression of fibrogenic genes such as LOXL2, collagen type I and TIMP-1, as well as down-regulate the expression of genes that promote inflammation such as CCR2 and MCP-1. In addition, histopathological data show that MN-001 can reduce fibrosis in a variety of animal models.
This Phase 2a clinical trial is a multicenter, proof-of-concept, open-label study designed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of MN-001 in NASH or NAFLD patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Subjects were aged between 21 and 65 years with histologically confirmed NASH, or imaging confirmed to be NAFLD, and patients with serum triglycerides greater than 150 mg/dL at the screening stage. Studies have shown that MN-001 can significantly reduce mean serum triglyceride levels from 260.1 mg/dL before treatment to 185.2 mg/dL after 8 weeks of treatment (p=0.00006). There were no clinically significant safety or tolerability issues during the study. After achieving the most important research endpoint, MediciNova will stop patient recruitment and research to accelerate the development of MN-001.
Dr. Yuichi Iwaki, President and CEO of MediciNova, commented: "We are very excited about the results of this study, which shows a significant reduction in triglycerides. Based on this result and our clinical studies from other indications Triglyceride data, we believe that MN-001 has the potential to benefit a wide range of patients with hypertriglyceridemia, not limited to NASH and NAFLD patients."
Reference materials:
[2] Phase 2 studies of two novel treatments for primary biliary cholangitis report encouraging results
[2] Gilead Presents Data on Multiple Investigational Regimens for the Treatment of Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Advanced Fibrosis at The International Liver Congress? 2018
[3] Arrowhead RNAi drug clears hepatitis B antigen in clinic
[4] MediciNova Announces Phase 2 Trial of MN-001 (tipelukast) in NASH / NAFLD will be Terminated Early based on Significant Positive Results from Interim Analysis
[Original Title: Inventory | Summary of Research Progress in Liver Diseases (No. 38)]
Suction blood vessel is also called vacuum collection blood vessel, according to the type of a total of nine categories. The details are as follows :1. Red head cover, no additives, used for the determination of some biochemical and immune indicators. 2. Yellow head cover, containing coagulant, can be used for biochemical and drug test determination. 3. Black cap, which is mainly used for the determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate. 4. Light blue cap for the determination of coagulation factors. 5. Green cap for blood gas analysis and hematocrit measurement. 6. Light green head cover, liver function, blood lipid, blood sugar and so on were measured. 7. Grey cap, which is a special test tube for measuring blood sugar. 8. Purple head cover, mostly used for determination, blood type, blood routine, glycosylated hemoglobin and so on. 9 orange head cover, used for the determination of serum, hormones and so on.
Type of blood vessel extraction:
1, red head cover, no additives, used for the determination of some biochemical and immune indicators.
2, yellow head cap contains coagulant, can be used for the determination of biochemical and drug tests.
3. Black cap, which is mostly used for determining erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
4. Light blue cap for the measurement of blood coagulation factor.
5, green head cap, for gas and blood analysis, hematocrit measurement.
6, light green head cover, liver function, blood lipid, blood sugar and so on.
7. Grey cap. This is a special test tube for measuring blood sugar.
8, purple head cover is used for determination, blood type, blood routine, glycosylated hemoglobin and so on.
9, orange head cover, mostly used for serum, hormone and other measurements.
Blood Collection Tube,Red Glass Plain Tube,Red Pet Plain Tube,Gel&Clot Activator Tube,Yellow Color Blood Tube
Changchun ZYF science and technology CO.,LTD , https://www.zyf-medical.com