The current fitness bracelet and heart rate detector products are relatively complete, but if you want to record the activities inside the body, these products still can not satisfy us. Lota Biosciences' millimeter-scale sensor can stay in the human body for a long time and transmit data wirelessly. Today the company received $15 million in Series A financing.
The team is from the University of California at Berkeley, and its co-founders Jose Carmena and Michel Maharbiz have worked to improve the workings of microelectrodes. Such devices have been used in various fields of medical and experimental science, primarily for detecting and stimulating nerves and muscle tissue. For example, brain microelectrode arrays can detect early signs of brain disease, and electrodes near the heart can accurately monitor heart rate.
Although the name is "microelectrode", it is not small enough. It is usually used on larger machines, and for many reasons, the microelectrode stays in the human body for less than a week.
To reduce the size of the electrodes, manufacturing technology and energy supply are two major issues. The two founders thought, why not design a better product?
Carmena said: "The first thing we think of is a non-stationary brain sensor transmitting node that is powered by radio frequency (RF)." But a fundamental problem quickly emerged, the wavelength of RF wireless electromagnetic waves is higher. Long (ranging from tens of centimeters to tens of meters) requires a larger antenna to receive, and the size of the antenna prevents it from flowing in the blood, so it has no practical value. “This is two orders of magnitude larger than what we expected,†he recalls.
But shortly afterwards, Maharbiz was able to solve this problem. "Sounds, you may not believe that when this inspiration appeared, I was in a parking lot. I just thought about it, and then everything was solved," he said.
Sound wave energy supply
Readers may be familiar with ultrasound, a diagnostic tool that helps doctors draw images of pregnant women's in-vivo—or more like a rangefinder tool that can reflect when an object is encountered. But recently this technology has been developed for a new use.
Compared with the RF radio waves mentioned above, the wavelength of the ultrasonic wave is micron, which means that the ultrasonic antenna captures it very efficiently. This means that the ultrasound antenna can get enough energy to keep the sensor working.
In addition, through the previous ultrasonic diagnostic technology, we can imagine that the ultrasound will directly pass through our body fluids, in contrast to the electromagnetic waves will be absorbed by these ion-rich, salt-rich body fluids. "Ultrasonics don't do this. For it, you're like a piece of jelly, it goes straight through," Maharbiz said.
With this technology, the construction of the device will be simple and the size will be very small. At one end is a piezoelectric crystal that converts kinetic energy (where the energy is applied to ultrasonic waves) into electrical energy. The center is a microchip surrounded by a circle of electrodes.
Because it is very small, it can be attached to nerve or muscle fibers. When the device is activated by the ultrasonic beam, a voltage is formed between the electrodes, and the internal current is affected by the activity of the biological tissue. These changes can be reflected by ultrasonic pulse reflection, and the signal receiver can reverse the change of physiological voltage through these changes.
Simply put, ultrasound supplies energy to the sensor and changes slightly after it is reflected back, depending on the activity of the nerve or muscle. You only need to continuously emit stable ultrasonic pulses, so the system can easily collect accurate data.
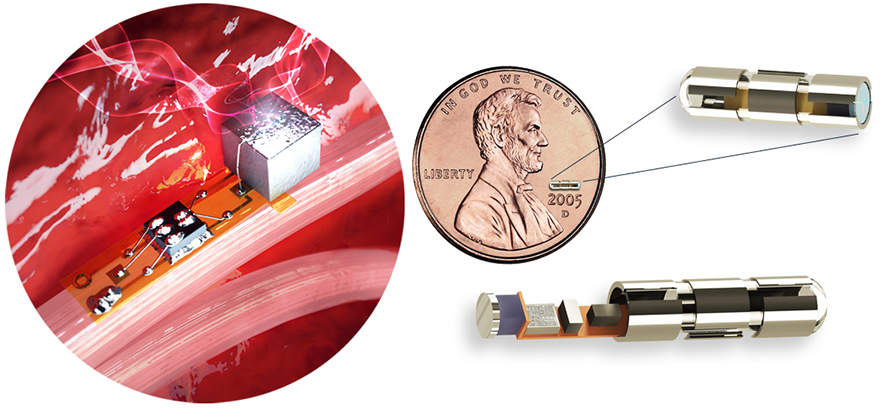
These sensor nodes are placed inside the container (the material of the container is not easy to react), and can be safely implanted into the body. The number of implants can be one or more than ten. It can detect the activity of myocardial fibers and control the prosthesis. . It can also be used for treatment because it produces voltage.
It should be noted here that this product has not been used in the brain. Although it does not say that it can't work in the central nervous system, its size must be smaller and the tests performed will be more complicated. It will first be used in the peripheral nervous system.
But before that, it needs to be certified by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Long road to medical technology
When any kind of thing has just been invented, it is impossible to get it immediately. In particular, such electronic devices implanted in the human body must undergo rigorous examination before they can be put into trial and practical.
In contrast, Lota is fortunate, it does not install a battery like the peers. Its energy supply and information transmission are all done by ultrasound, and decades of research have ensured the safety of this technology.
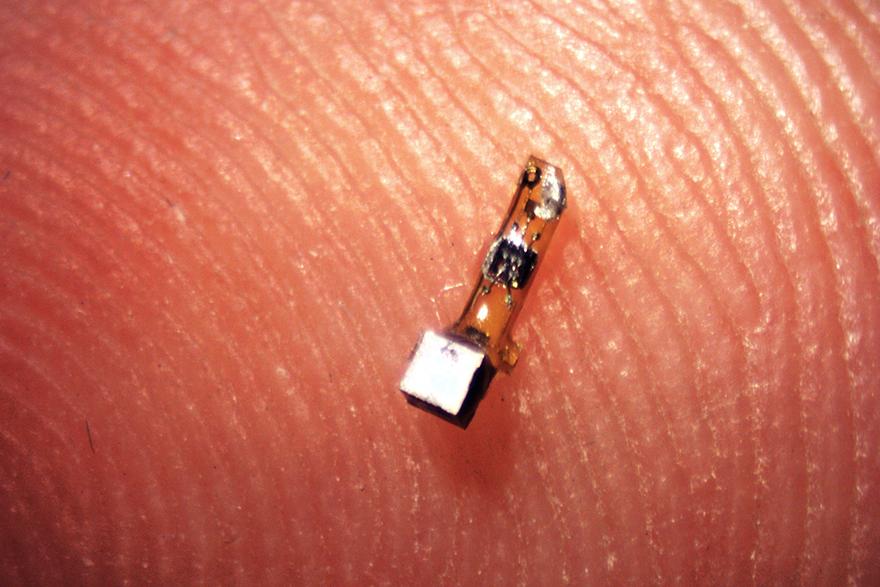
"The FDA has clearly defined the average power and ultimate power that the human body can withstand. We are far from dangerous bands and power, and we don't use any rare technology or materials. Continuous low-power ultrasound will not give What impact do we have.†Maharbiz explained. And the removal of the lota sensor is much simpler than other implanted devices. It can be removed by laparoscopy or minimally invasive surgery.
This is the advantage of lota, but the experiment can not be rushed. The team's work began in 2013 and is far ahead of other companies. In order to enter the human trial phase as early as possible, Lota received the financing, including Horizons Ventures, Astellas, Bold Capital Partners, Ironfire and Shanda. This round of financing was completed in May and was not announced until today.
The financing will help the company save nearly 18 months to submit the product version for production to the FDA as soon as possible to obtain more financing to support trials in the next few years.
Beverage Fiber,Polydextrose Fiber,Bulk Nutrients Polydextrose,Litesse Polydextrose
Qingdao Bailong Huichuang Bio-tech Co., Ltd. , https://www.sdblcycn.com