"Lancet" issued 5 reasons for Chinese early death: the prevalence of liver cancer exceeded expectations
June 27, 2019 Source: Global Science
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];Recently, The Lancet released a large-scale analysis of the disease burden and risk factors affecting Chinese people in the past 40 years. Among them, stroke, ischemic heart disease, liver cancer, lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are the five major factors for premature death in China. In terms of risk of illness, smoking ranks among the top risk factors in 21 provinces and ranks among the top three in the remaining provinces. The risk of some risk factors is rising, especially high blood sugar, high blood pressure, high body mass index (BMI) and outdoor air pollution in many provinces.
Since the 1990s, with the rapid growth of China's economy, the standard of living of the people has also been greatly improved. At the same time, more advanced medical technology and a better medical system are quietly changing the way we deal with disease. Changes in these basic conditions are also affecting the country's disease types and health risk factors. As early as 2016, the Chinese government proposed the “Healthy China 2030†program. The main goal of the plan is to improve life expectancy and health expectations and increase disease prevention measures in the next 10 years.
In the latest study published in The Lancet, the team from the China Center for Disease Control and Prevention pointed out a clear direction for the plan, which diseases and risk factors can improve the national health. For example, the most important factor affecting Chinese health in 1990 was infectious disease, which has now turned into non-infectious chronic diseases such as high blood pressure. Chronic diseases such as stroke and ischemic heart disease have replaced the previous lower respiratory tract infections and neonatal diseases, becoming a new type of disease that affects healthy life expectancy.
The first few common risk factors are high blood sugar concentration, high blood pressure, high body mass index (BMI), and some provinces are also among the air pollution particles. Zhou Zheng, deputy director of the China Center for Disease Control and Chronic Diseases, said: "China has come to a key turning point after more than 30 years of development. In the future, many chronic diseases, especially chronic diseases of the elderly, will become China's primary disease burden. More than infectious diseases."

Eating habits are affecting the health of Chinese people. Image source: pixabay
This study analyzed the health effects of diseases in various provinces of China in terms of life loss years (YLLs), disability survival years (YLDs), and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and the health policies of different regions in the future. The execution direction provides an important reference value.
Stroke, liver, and lung cancer are becoming the top health killers
In 2017, the top five diseases affecting YLLs were stroke, ischemic heart disease, lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema), and liver cancer. The most notable of these are lung cancer and liver cancer, and between 1990 and 2017, their YLLs and mortality rates are rising.
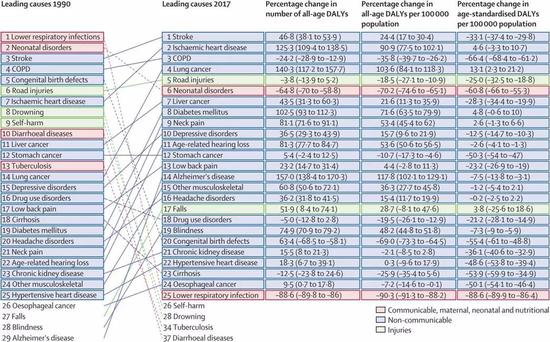
With the changes in the age structure of the society, many elderly diseases have begun to appear in the forefront of the impact of YLDs, such as musculoskeletal disorders, mental degenerative diseases and sensory organ diseases. The researchers pointed out that such geriatric diseases have not yet attracted enough public attention, but musculoskeletal diseases usually seriously impair the patient's activities and labor capacity, and will become the main burden of future medical resources.
Stroke and ischemic heart disease also accounted for the first two factors affecting DALYs, and in 1990 the first two were lower respiratory tract infections and neonatal diseases. In addition, research indicates that hypertension is becoming the leading killer of health. In 2017 alone, 2.54 million people died of hypertension-related diseases, 95.7% of which were cardiovascular disorders.

Image source: Lancet
It can be seen from the trend chart that the effects of infectious, maternal and infant-related diseases on DALYs are declining. The DALYs caused by injuries are also decreasing, and the effects of drowning and self-harm have decreased by 71.3% and 71.8%, respectively. At present, the main types of diseases affecting Chinese health are basically non-infectious chronic diseases.
Differences between regions
Among the 20 disease factors affecting YLLs, only Beijing and Macao are all below the national average and are among the healthiest regions. In addition, most of the diseases with a lower rate of disease than the national level are Shanghai and Hong Kong. However, the researchers said that comparing the measured data with the expected data, the impact of diseases on DALYs in many areas of China was lower than expected, and 12 provinces were even more than 30% lower than expected. The result is more comprehensive health over the years. Intervention plans and medical level improvements are inseparable.
These provinces or municipalities include Chongqing (-37%), Anhui (-35%), Zhejiang (-33%), Fujian (-33%), Shanghai (-32%), Guizhou (-32%), and Ningxia (- 31%), Jiangsu (-30%), Hainan (-30%) and Beijing (-30%).
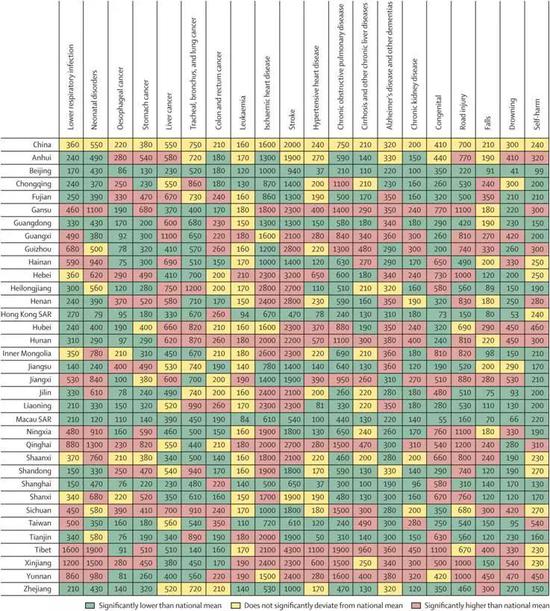
The red color in the figure is the average rate of disease. For example, more than 10 diseases in Hunan, Yunnan and other provinces have higher impact on YLLs than the national average.
However, it is worth noting that the impact of liver cancer on DALYs is unexpectedly high in all provinces. The prevalence of liver cancer in all provinces is higher than that of the same level of development. The ratio of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) is based on The development level calculates the expected value of 3 to 8 times. As can be seen from the chart, Guangxi, Sichuan and Heilongjiang are all major liver cancer provinces.
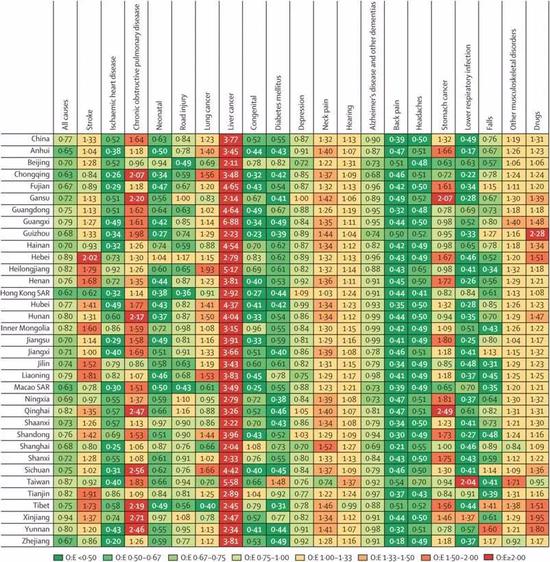
The situation of liver cancer is extremely severe. From the big red column in the picture, the incidence of liver cancer in all provinces is seriously exceeded.
Smoking, diet, and exercise are the main health methods for the future
In terms of risk prevention and control, the study suggests that the health effects of smoking are still very serious. Moreover, the analysis also yielded some unexpected results. For example, many previous studies have suggested that there is a link between excessive sodium intake and high blood pressure. China's health policy propaganda for many years has already led to a decline in sodium intake in the diet of ordinary people, but the risk of hypertension in 16 provinces has not decreased. Therefore, research suggests that tobacco control and blood pressure control should be one of the primary health goals for the next 10 years.

Image source: Lancet
In addition, between 1990 and 2017, the improvement of living standards and changes in living habits significantly changed the body mass index of Chinese people. Excessive consumption of red meat (pig, cow, lamb) in daily life, lack of bad habits such as exercise The proportion of diabetes is gradually rising and is becoming the next healthy killer.
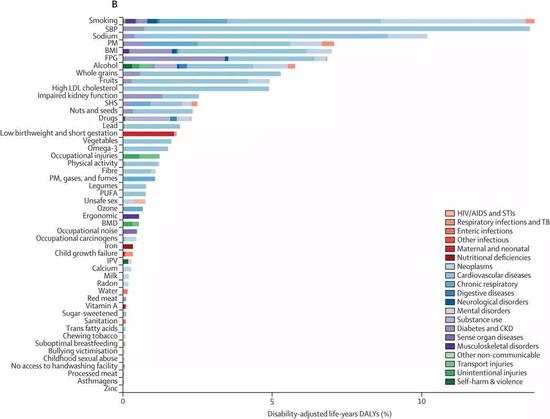
The top three risks affecting Chinese health are smoking, high blood pressure and sodium intake.
For air pollution problems, the study also showed optimistic predictions that air pollution-related cancer or respiratory diseases will be contained in the future as traditional energy sources transition to clean energy. In the next five years, the concentration of PM2.5 particles will be reduced by 25%, 20% and 15% respectively in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta regions. Beijing is striving to control the concentration below 60μg/m3.
The research of "Lancet" has played an important guiding role in the implementation of "Healthy China 2030". Many regions can formulate countermeasures according to the severity of different diseases. Dr. Liang Xiaofeng, deputy director of the China Center for Disease Control and Prevention, also said, “The results of these detailed provincial studies will help us tailor our health policy to local health needs.†Of course, the public should also correct bad habits based on guidance. The responsibility for personal health still needs to be picked up by oneself.
X Ray Short Lead Apron,0.35Mmpb Short Lead Apron X-Ray,0.5Mmpb Xray Short Lead Apron,Xray Protection Short Apron
Longkou Kangxie Medical Instrument Co., Ltd , https://www.kangxiemedical.com