1. Identify the color of chicken legs and mouth (yellow leg and yellow mouth before laying eggs). For high-yield chickens, the higher the faded egg production rate is, the higher the egg production rate is from 250 to 300 days old, which is the low-yield chicken with yellow legs and yellow beaks, and even without laying hens. Chickens that produce white shell eggs have yellow legs and mouths; chickens that produce pink shell eggs have brown legs and mouths.
2, distinguish from chicken cocks. High-yield chickens have large red, soft, delicate temperatures, one side, and normal red color. Low-producing chickens, even chickens that do not produce eggs, do not fall down, have white spots or white frost, and have thin crowns. If you have Marek's disease, the chicken's crown is atrophic, there is no temperature, and the crown is cool; if you have a purple crown and a black crown, the chicken should be eliminated in time.
3, distinguish from feathers. High-yielding chicken feathers are earthy, unkempt, unsmooth, non-smooth, with high-yielding chickens that have feathers that fall off the neck, back, and chest, or are disfigured. If they are often dressed in smooth hair, such chickens are low-yielding chickens.
4, distinguish from the anus. The anal laxative muscle relaxes, elasticity around the expansive contractor muscles, a moist sensation, and immediate contraction, outflow of viscous secretions, such chickens are high-yielding chickens. There is no elasticity in the contraction of the anus and extrusion around the abdominal muscles, and there is no sense of moisture for the low-yielding chickens.
5, distinguish from the eating situation. When feeding, high-yield chickens, such as hungry tigers, devour, have a strong appetite, do not look up when they eat, do not picky eaters, and eat quickly. Picky eaters do not like to eat, even if the chickens that the feed does not eat are low-yielding chickens, or even eggs.
6, distinguish from the feces. The high-yielding chicken droppings are shaped into small white heads and drink more water in the summer. They are also basically formed and the colors are normal. Low-producing chickens and non-laying hens have slender feces and dry feces.
7. Distinguish from the pubic bones. High yield chicken pubic bone 3 to 4 fingers. Low-producing chicken pubic bone 2 refers to even 1 finger.
8, distinguish from the abdomen. The high-yielding chicken has a large belly. The low-yielding chicken has a narrow, thin, thin sternum with a sharp blade.
9, chicken thief discrimination. Handling chickens that eat eggs: For chickens that lay eggs on the upper layer, they can be transferred to the upper cage; chickens that use the ticks on the neck should be eliminated or placed in single cages.
10. Distinguish from chicken roar. The roar of high-yield chickens is neat and uniform, indicating that the laying hens are healthy. Chickens that do not produce eggs for a long period of time do not call or send whistles. When abnormal animals and other small animals are found in chicken farms, they immediately scream and cause large groups to frighten and produce soft eggs.
1. Frame :high quality section steel welding,The surface electrostatic spray, durable, beautiful and generous.
2. Bed panel is made of molding cold rolled steel, surface electrostatic spray, corrosion resistant, easy to clean.
3. Head & foot board:use ABS high quality engineering plastics and stainless steel pipe, lined with fireproof board, beautiful appearance, soft color . easy to removed.
4. Caster:use Taiwan Shi Ke Rui control wheel,No noise, Convenient mobile, four wheel synchronous braking system, lock solid.
5. Guardrail : ABS lifting guardrail, 4-piece, When not in use can be hidden in the bed.
6. Handle:ABS hidden handle
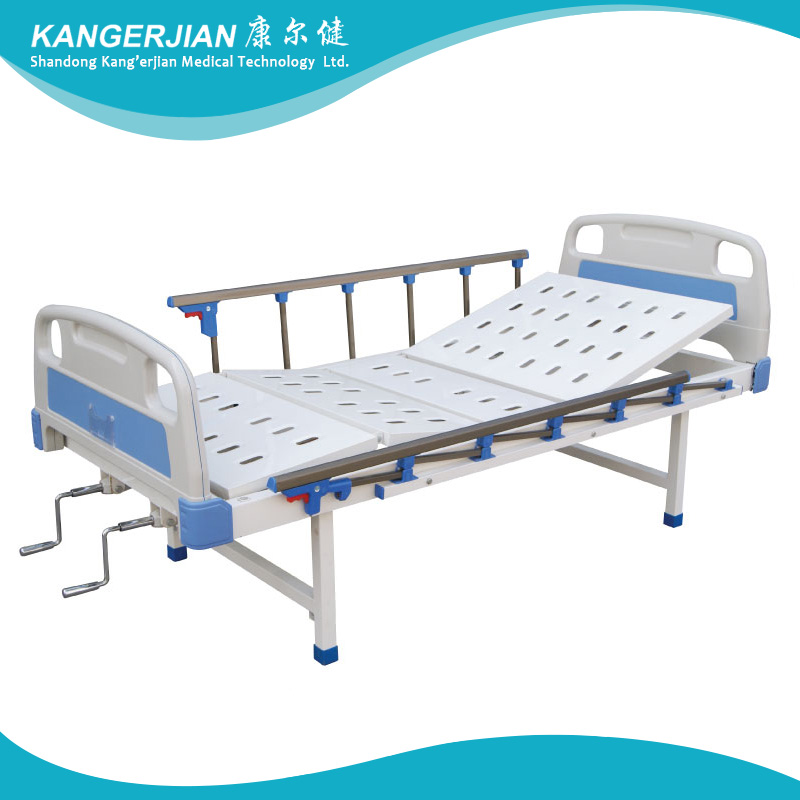
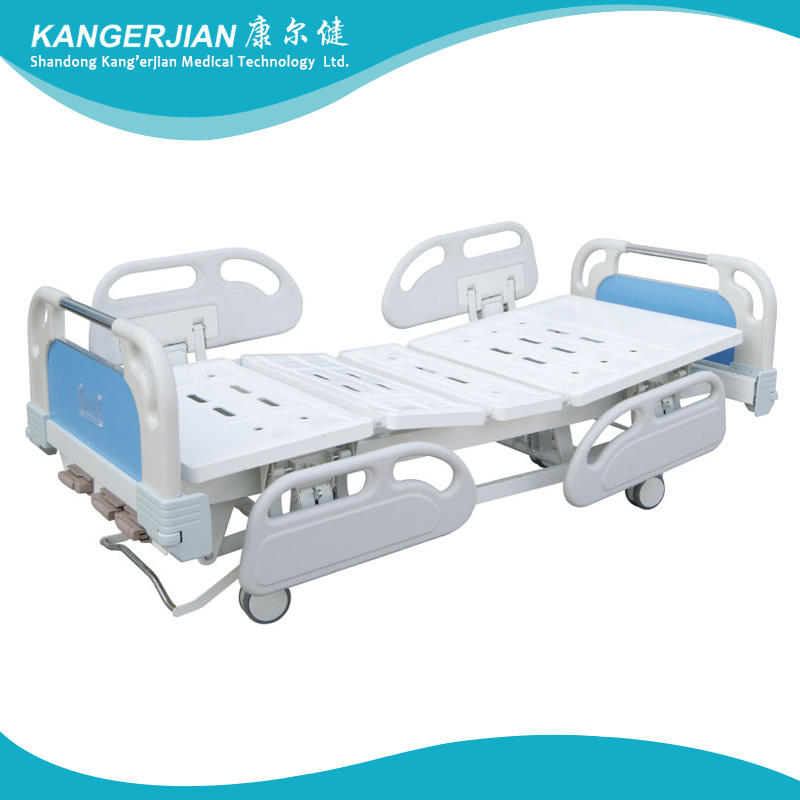

Manual Hospital Bed,Manual Hospital Equipment Bed,Manual Lift Hospital Bed,Functions Manual Hospital Bed
Shandong qufu healthyou Medical Technology co.,Ltd , https://www.kangerjianmedical.com