Evelyn Goh
Waters Pacific, Singapore
Application advantage
This method can simultaneously analyze 12 water-soluble vitamins:
- An alternative time-consuming single compound microbial assay.
- Low concentrations of target substances (especially vitamin B12) are detected in complex matrices such as infant formula.
- MRM and full scan data can be obtained simultaneously in one analysis.
Waters Solutions
ACQUITY UPLC® System
Xevo® TQ MS
MassLynxTM software
TargetLynxTM application software
IntelliStartTM technology
RADARTM
Key words
Water-soluble vitamins, vitamin C, B3, B6, B12, B1, B9, B2, B7
Introduction
Vitamins are a trace element that can only be taken through food because it cannot be synthesized in the human body. Vitamins in infant formula are particularly important for the healthy growth of infants, especially for infants who are unable to breastfeed and use formula as their primary source of nutrition. The official water-soluble vitamin testing method is based on proceduralization, mainly microbial identification, which has been used for nearly a decade. For the purpose of extraction, each vitamin is analyzed separately to determine its total content in the food. This usually takes a lot of time.
It is very difficult to simultaneously analyze the vitamins in infant formula added with nutrients using a test method because:
- Diverse vitamin structure and complex chemical composition
- Low vitamin content
- Matrix complex
- Unstable under light and heat
- Solubility problem
- Wide range of concentrations in formula
In this application note, we will introduce a fast UPLC®/MS/MS mass spectrometry method that takes only five minutes to simultaneously detect 12 water-soluble vitamins in infant formula using the ESI positive mode.
experiment
During the sample preparation and analysis phase, all solvents are stored in the dark at temperatures below 5 ÌŠC. Vitamin standard solutions are prepared daily.
Liquid phase condition
LC System: ACQUITY UPLC System Column: ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3
2.1 x 50 mm , 1.8 μm
Column temperature: 40 °C
Sample temperature: 4 °C
Flow rate: 0.6 mL/min
Mobile phase A : 10 mM ammonium formate + 0.1%
Aq. formic acid mobile phase B : 10 mM ammonium formate + 0.1%
Methanol solution gradient:
Time (minutes) | %A | %B |
0.0 | 99 | 1 |
2.0 | 99 | 1 |
3.0 | 45 | 55 |
3.1 | 1 | 99 |
4.0 | 99 | 1 |
5.0 | 99 | 1 |
Total running time: 5.0 minutes Injection volume: 10 μL, fully filled loop
Mass spectrometry condition
MS System: Xevo TQ MS
Ionization: ESI+
Capillary voltage: 1.0 kV
Source temperature: 150 °C
Solvent removal temperature: 600 °C
Desolvent Gas: 1200 L/ hr
Acquisition: Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM)
And RADAR full scan collision gas: argon 3.5 x 10-3 mbar
Standard addition method
When blank samples are not available, quantitative analysis of water-soluble vitamins in infant formula will be carried out by standard addition methods (except nicotinamide)*. Add a known concentration (standard solution) of the analytical solution to the sample so that any matrix effects can be eliminated during calibration. The analyst did not initially know the amount of analyte in the sample, but could track the amount of standard solution added and the change in instrument response after the standard solution was added. Therefore, the concentration of the analyte in the sample can be determined by the extrapolation of the calibration curve. In practice, the addition volume of the standard solution needs to be kept at a small level to avoid dilution of the sample matrix.
* The sample matrix uses the existing dilution factor (see experimental procedure), no standard addition, the instrument's response to nicotinamide (B3) in infant formula is close to the detector saturation. If the standard addition method is used for nicotinamide, the detector will be saturated.
Sample preparation, extraction and standard addition
Prepare according to the three-fold concentration on the package instructions for infant formula.
Place 10 ml of infant formula solution in a foil covered polypropylene (PP) tube; add 20 ml of 100% ethanol.
Shake and mix for 2 minutes and centrifuge at 3500 RPM for 15 minutes.
The supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm PVDF filter.
Transfer 20 μL of the supernatant to the vial, add 10 μL of a known standard concentration solution containing 11 analytes, add water to the sample vial to 1 mL (diluted the analyte in the sample matrix by 50 times; the analyte in the standard solution is finally Dilute 100 times).
The nicotinamide standard curve in the solution was prepared separately.
Analysis by LC/MS/MS.
Acquisition and data processing methods
Data is obtained through the MassLynx software v.4.1 version and data processing is performed using TargetLynx application management software.
Optimize automatic MRM acquisition methods for 12 target vitamins using IntelliStart technology. IntelliStart simply enters the basic information of the complex to automatically find the parent ion, optimize the cone voltage, find the daughter ion and optimize the collision energy.
The two MRM channels for each vitamin have been optimized; the first channel is the quantitation ion channel and the second channel is the qualitative ion channel. The channel's dwell time is automatically optimized with a minimum of 12 points per peak to ensure quantitative reproducibility. The MRM channel, cone voltage, collision energy, and retention time of the analyte are detailed in Table 1 below.
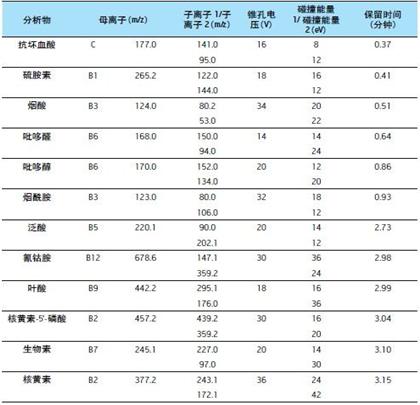
Table 1. LC/MS/MS parameters for the detection of water-soluble vitamins
In addition to MRM data, full scan data is available using the RADAR mode of the Xevo TQ MS. RADAR is an acquisition method that can obtain rich information. It can obtain the background mass spectrum information of the sample matrix in real time while acquiring MRM data. Using RADAR does not affect the quality of MRM data.
Results and discussion
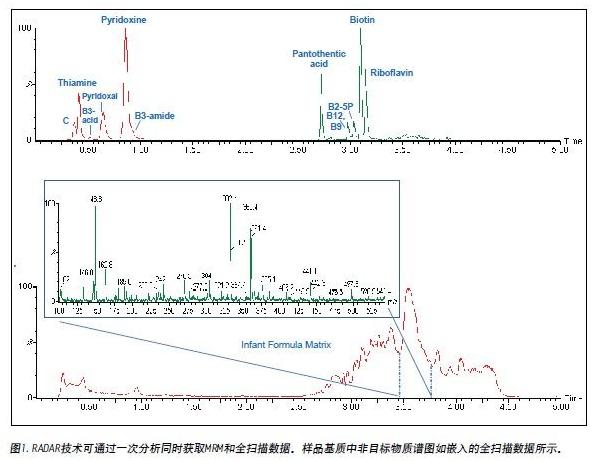
The ACQUITY UPLC System successfully analyzed 12 water-soluble vitamins in combination with the ESI positive ion mode of the Xevo TQ MS. Use ACQUITY UPLC to quickly separate all analytes in 5 minutes, including 1 minute equilibration time, as shown in Figure 1.
In the same analytical test, the full-scan mass spectrometry information of the compounds in the infant formula matrix was monitored using the RADAR mode of the Xevo TQ MS. RADAR uses the fast acquisition rate of the Xevo TQ MS to obtain full scan MS data, while simultaneously obtaining enough analyte peaks in MRM mode for accurate quantification and characterization.
The RADAR can be used to observe impurities in the sample matrix and to understand the content and type of compounds that may cause matrix effects. This helps in optimizing the LC-MS/MS method development process to reduce matrix effects. For example, the target peak can be separated from the region that may cause matrix influence or ion suppression by adjusting the separation method. The insert in Figure 1 is a mass spectrum extracted from the full scan data of the infant formula sample matrix.
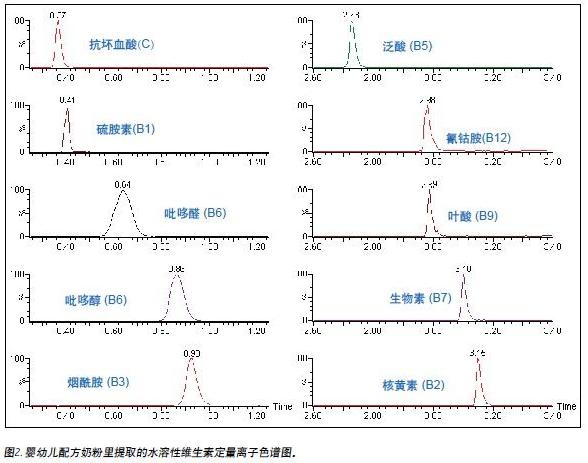
This method detects two different popular brands of infant formula. Figure 2 shows a quantitative ion chromatogram of water-soluble vitamins extracted from one of the brands.
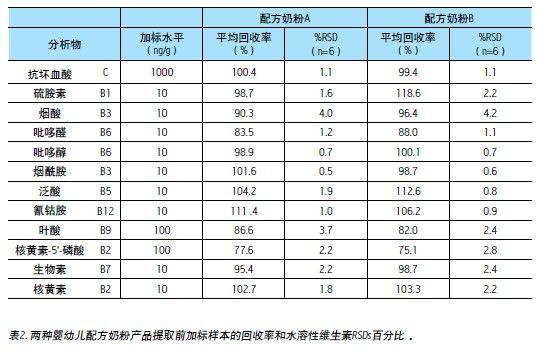
Recovery and reproducibility
The recovery rate was obtained by comparing the sample before the extraction and the sample after the extraction. Two different brands of infant formula were tested in two days and repeated six times a day.
Most of the compounds in infant formula reached ≥90% extraction recovery, except pyridoxal, folic acid and riboflavin-5'-phosphate. The main reason for the relatively low recovery rate is the water solubility of the above substances. Poor sex.
Although infant formula is a very complex matrix, the relative standard deviations (RSDs) of the six replicates are still below 5%. This shows the high reproducibility and stability of the method.
Linear and quantitative
Linear dynamic range, sensitivity and suitability can be evaluated by standard addition methods. A major advantage of the standard addition method is that it avoids the determination of matrix effects and eliminates the effects of ion suppression.
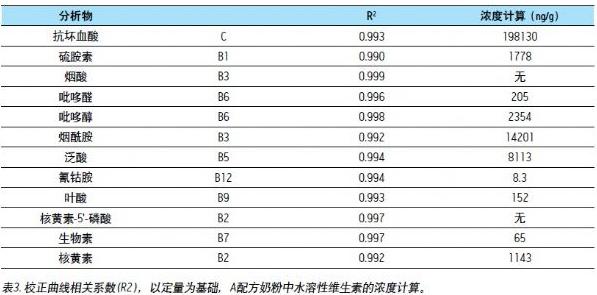
A good linear relationship with a correlation coefficient ≥ 0.99 is obtained. As shown in Table 3, the concentration range of infant formula for all analyses is different: ascorbic acid (C) is 10 - 10000 ng/mL; cyanocobalamin (B12) is 0.1 - 10.0 ng/mL; the remaining analytes ranged from 1 to 100 ng/mL. Data 3 shows the calibration curve for an infant formula ascorbic acid (C) and cyanocobalamin (B12) based on the standard addition method.
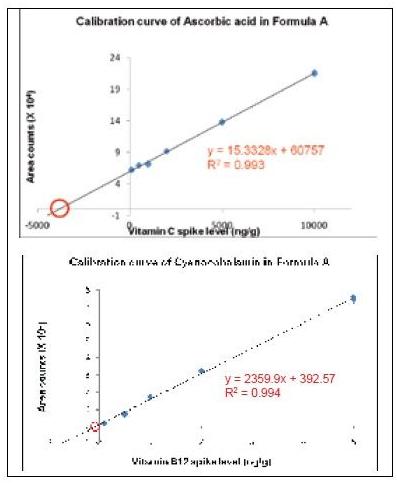
Figure 3. Ascorbic acid and vitamin B12 calibration curves for Formula A milk powder using standard addition methods .
The calibration curve is extrapolated. The absolute value of the x-axis intercept indicates the concentration of the analyte in the infant formula due to the dilution factor (50 x). The sensitivity of the Xevo TQ MS allows us to dilute the sample to reduce matrix effects while still detecting the target compound.
in conclusion
One using the ACQUITY UPLC and Xevo TQ MS ESI positive mode 5 minute rapid assay for simultaneous analysis of 12 water soluble multivitamins. This method replaces the time-consuming vitamin analysis alone. By combining different vitamin analysis methods, the laboratory can increase sample throughput, reduce volumetric consumption, and reduce operating costs.
The high sensitivity of the Xevo TQ MS enables the detection of low concentrations of target analytes (especially cyanocobalamin), such as infant formula, in very complex matrices. The Xevo TQ MS achieves a low limit of quantitation and dilutes the sample to reduce matrix effects.
RADAR technology monitors matrix interference, impurities and degradants in the sample while accurately quantifying target analytes. Analysts can make accurate decisions when detecting matrix effects and can accurately assess the presence of matrix effects.
IntelliStart technology simplifies system preparation and MRM method development, ensuring that scientists at all levels can operate instruments quickly and accurately, producing the highest quality reproducible UPLC/MS/MS data.
references
1. AOAC Official Method 985.32, Microbiological Method for Analysis of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxal, Pyridoxamine) in Ready-to-feed Milk-based Infant Formula.
2. AOAC Official Method 992.07, Microbiological Turbidimetric Method of Pantothenic Acid in Milk-based Infant Formula.
Sterile Serum Vials are produced by aluminum caps, non-latex butyl stoppers and clear SCHOTT Neutral Type I glass vials. The production process of sterile Serum Vials is carried out under strict Class 100 workshop. Finished vials can meet the FDA`s authorised 14-day sterility test.Sterile serum vials are primarily used for mixing different medications or solutions for injection or research applications like HCG, heparin, lidocaine, diabetic medications and morphine for intravenous or syringe injections.
Sterile Serum Vials
Sterile Serum Glass Vials,Serum Vials,Glass Serum Vials
China Lemon Trading Co.,Ltd , https://www.lemonvial.com