The adeno-associated virus belongs to the family Parvovirus and is a non-enveloped single-stranded linear DNA virus with a genome size of approximately 4.7 kb. The use of adeno-associated virus can transfer foreign genes into animal tissues and cells, and has many advantages such as high safety, low immunogenicity, wide host range, and stable expression, and is widely used in animal research.
There are many serotypes of adeno-associated virus (12 species ) , and different serotypes have different affinity for different tissues. Therefore, specific research, the following problems are often plagued by scientific researchers: what serotypes choose? How to inject? How many viruses are injected? How to choose the injection site? How long does the injection test?
This article provides a simple summary of common injection sites ( brain, retina, liver, heart and arteries, lungs, kidneys, muscles, intestines ) and methods to provide a concept and ideas.
First, the brain
The commonly used serotypes of brain tissue are AAV1, AAV2, AAV5, AAV8 and AAV9, among which the common serotypes of nerve tissue are AAV2, AAV5 and AAV8. For brain tissue, AAV5 is more widely used and AAV8 is more effective (notably, AAV5 is more effective in monkey neural tissue). In terms of effect, AAV8 is larger than AAV1.
Different serotype targeting of AAV is different for different parts of brain tissue:
1) Hippocampus: AAV9 is more effective than AAV8;
2) Different cells of different nerve tissues, different serotypes have different targeting: serotypes commonly used in neurons include AAV1, AAV2, AAV5 and AAV9; serotypes commonly used in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes have AAV1 and AAV5.
Overall, AAV2 is widely applicable in all tissues and is also reflected in brain tissue, for example, it can reach 75% of brain tissue. AAV2, AAV5, AAV8 and AAV9 are also common and should be carefully selected according to different organizations. Here are a few special cases:
1. The Enteric Nervous System (ENS) is a complex network of nerve cells that spreads throughout the gastrointestinal digestive tract. The number of neurons is comparable to that of the spinal cord (about 100 million nerve cells). The nervous system is in the lower part of the human trunk and belongs to the vagus nerve. It is distributed in the form of a thin layer between the digestive muscles to regulate digestion. Commonly used AAV5, AAV6, AAV8 and AAV9, AAV6 has certain targeting to intestinal glia and neurons. The injection site can be selected for descending colon, injection volume and titer: 5 μl of virus with a titer of 1.3 × 10^12 GC/ml can be injected. Detection time: expression was started 2 weeks after injection and tested at 2-6 weeks.
2, the common serotype of brain tissue is AAV9, injection method: left ventricular injection or lateral ventricle injection. Injection dose and titer: Select a virus solution with a titer of 0.5–4.0×10^11 GC/ml, dilute to 100 μl, and start testing two weeks after injection (14d). The picture below shows some brain tissue injections:
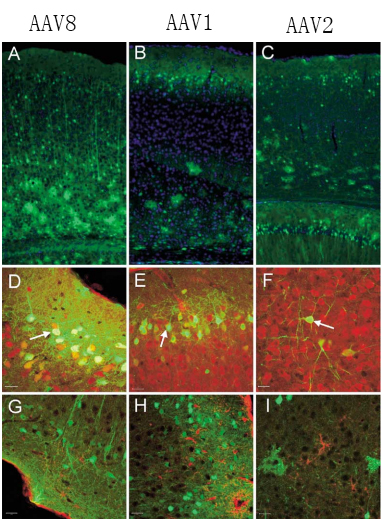
Fig1. Transduction and phenotyping of transduced cells in the cerebral cortex
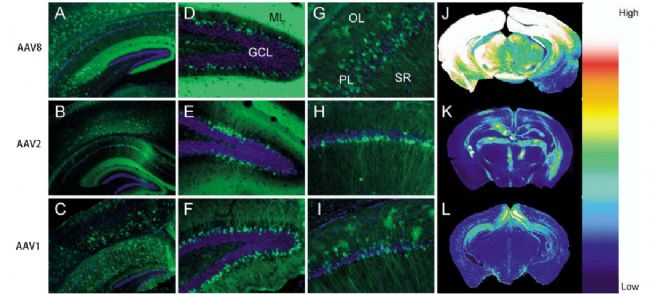
Fig 2. Transduction of cells in the hippocampal formation.
Neuroscience 138 (2006) 501–510
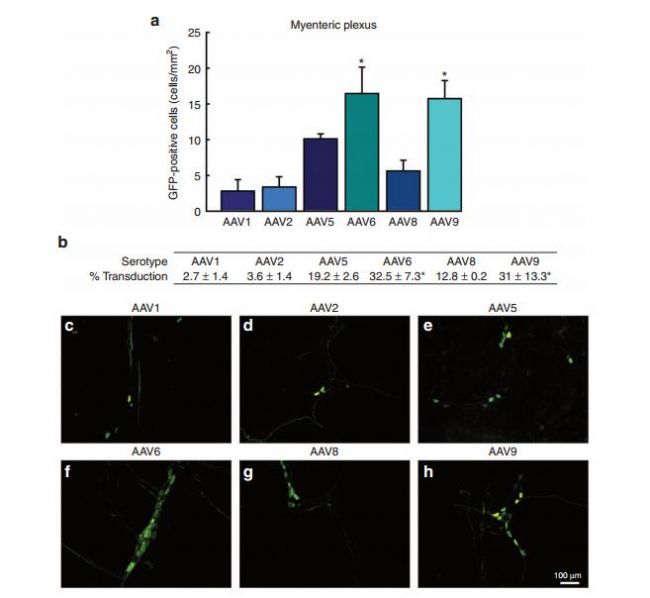
Fig. Transduction efficiency of recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) in the myenteric plexus (MP) of the enteric nervous system: a comparison across serotypes 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9
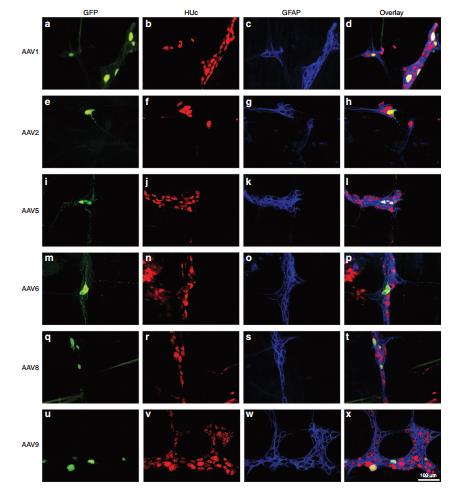
Fig4. Neuronal tropism of recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) transduction in the submucosal plexus (SMP): serotypes 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9.
Molecular Therapy vol. 23 no. 3 mar. 2015
Second, the retina
Common serotypes of retinal tissue are AAV1, AAV2 and AAV5. Because of its special nature, retinal tissue has its own characteristics: the injection success rate is 20-30%, which is easy to cause inflammation and damage of the retina. After injection, 1% atropine (and a small amount of neomycin, polymyxin B sulfate and Dexamethasone eye ointment is applied to the eyes, prolonging pupil dilation time, reducing glandular secretion and reducing inflammation, and is used continuously for 3-5 days. Its commonly used injection volume is 0.5 μl, and the virus titer is 1.5×10^7 GC/ml. Common injection methods: subretinal or vitreous injection.
However, different serotypes have different characteristics: AAV1 mainly acts on retinal epithelial cells, which can be detected 2-4 weeks after injection; AAV2 mainly acts on photoreceptor cells, retinal epithelial cells and vitreous, and AAV2 vitreous is widely distributed after injection, 2-4 weeks It can be detected; AAV5 can act on retinal epithelial cells and photoreceptor cells, and express AA5>AAV2 in photoreceptor cells for 2-4 weeks. The picture below shows the injection of some retinal tissue:
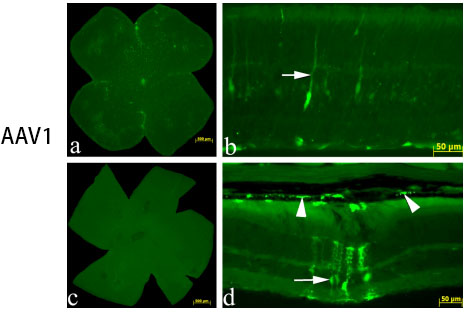
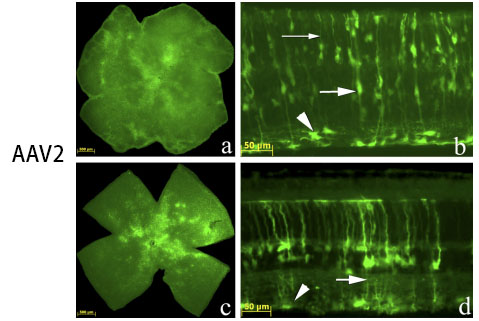
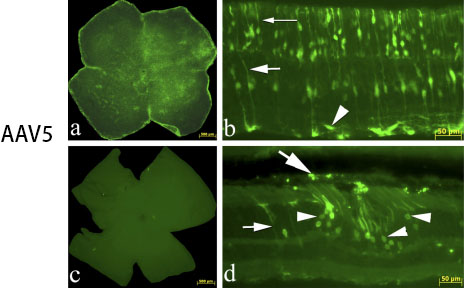
Fig 5. AAV added to the retinal ganglion cell surface in culture vs. intravitreal injection in vivo.
Vision Research 48 (2008) 377–385
Third, the liver
AAV2, AAV5, AAV7 and AAV8, of which AAV7 and AAV8 are 10-100 times more efficient than AAV2. The portal vein, peripheral vein, and tail vein are often selected at the injection site. Injecting virus titer is generally 8×10^10-2×10^12 (GC/kg) (human, primate); 1×10^11 GC/mouse, diluted to 50-100 μl for tail vein injection It can be tested after 2 weeks of injection. The picture below shows some cases of liver injection:
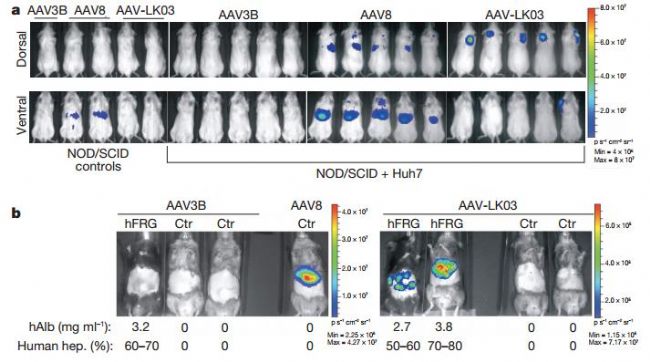
Fig 6. In vivo vector specificity analysis
Fourth, the heart and artery
For the heart and arteries, the commonly used serotypes are: AAV1, AAV6, AAV8 and AAV9. Among them, AAV2, AAV5, and AAV7 can also be used, but the expression is relatively slow, and the expression level can be equivalent to the expression of AAV1 and AAV6 after 3 months. AAV8 and AAV9 were most effective in all serotypes, and the highest expression was achieved in about 2 months.
Common injection sites are the coronary arteries, the aorta, the myocardium, and the tail vein. The injected virus titer was 1.9×10^11-10^12 GC/ml, diluted to 100 μl-250 μl (rat dose slightly higher than mice) injection; but for cardiac origin injection, 10^10 was often used. GC/ml virus titer, diluted to 20 μl. Detection time: It can be detected after 2 weeks. The picture below shows some cases of injection:
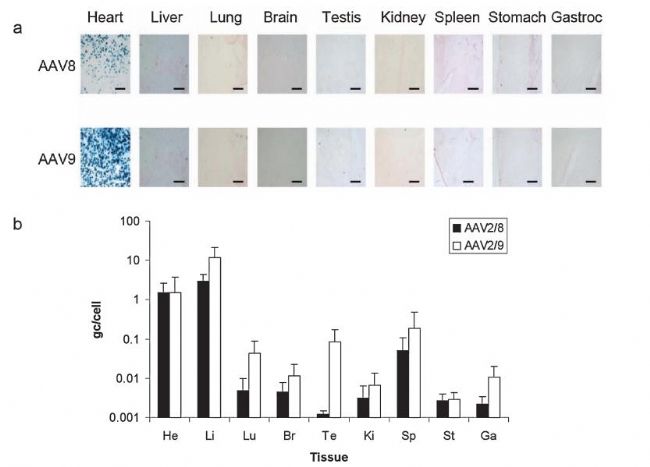
Biodistribution of LacZ expression and vector genomes 4 weeks after direct injection of 5 × 10 11 vg of AAV8- and AAV9-CB-LacZ into the rat heart., heart; Li, liver; Lu, lung; Br, brain; Te, testis Ki, kidney; Sp, spleen; St, stomach; Ga, gastrocnemius.
HUMAN GENE THERAPY 19:1359–1368
Fifth, the lungs
Common serotypes in the lungs are AAV1, AAV2, AAV5, AAV6 and AAV9. Because of the large distribution of sialic acid receptors on the surface of the lungs, AAV5 is more commonly used; in contrast, AAV2 and AAV6 are equally efficient. Common injection methods include nose drops, aerosol inhalation or intratracheal injection. The virus titer is 10^12 GC/ml, diluted to 3 μl, and the expression can be detected 2 weeks after the injection. The picture below shows some cases of injection:
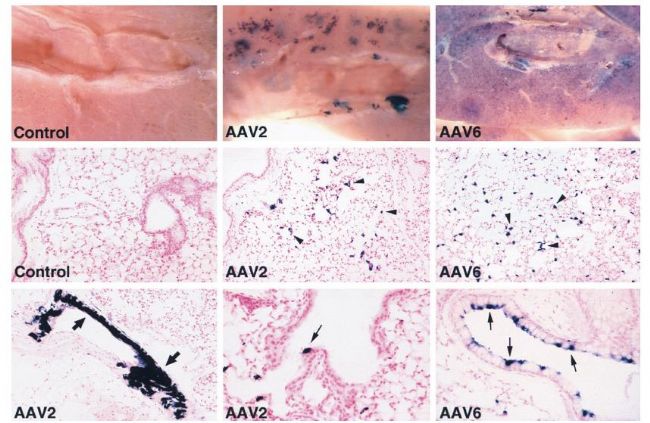
Histochemical detection of AP expression in mouse lungs 1 month after vector exposure.
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2000, p. 1524–1532
Sixth, the kidney
Common serotypes of the kidneys are AAV2, AAV8 and AAV9. The titer of the injected virus is generally selected from 1-5×10^11 GC/ml, and diluted to 50-200 μl for injection. Common injection sites include renal artery, renal vein, left iliac vein, and abdominal aorta. The expression can be detected after 2 weeks of injection. The picture below shows some cases of injection:
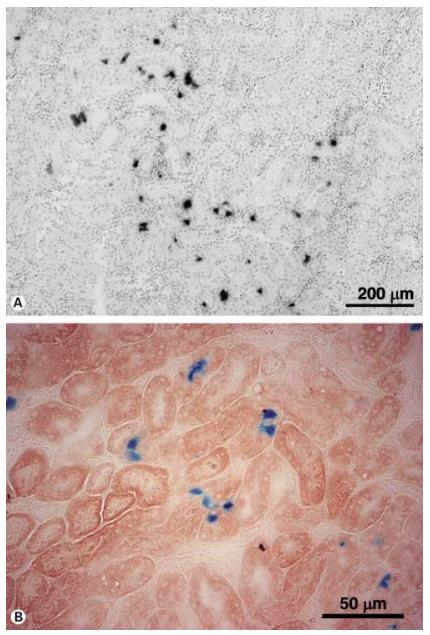
In vivo long-term transduction by AAV serotype 2 vector into the rat kidney.
Nephron Exp Nephrol 2004;96 :e119–e126
Seven, muscle
The commonly used serotypes for muscle tissue are AAV2, AAV8 and AAV9. Among them, AAV8 and AAV9 are the most commonly used, as are the myocardium, pancreas and adrenal glands. Skeletal muscle is divided into fast and slow muscle fibers, AAV2 is often applied to slow muscle fibers, and AAV6 is effective for both. The doses of the mice were different for different ages: the amount of virus selected by the young rats was 7×10^10-1.2×10^11 GC/g; the amount of virus selected by the adult mice was 3.5 × 10^11-7× 10^12 GC/only; but low doses of AAV9 did not reach all cardiomyocytes. The picture below shows some cases of injection:
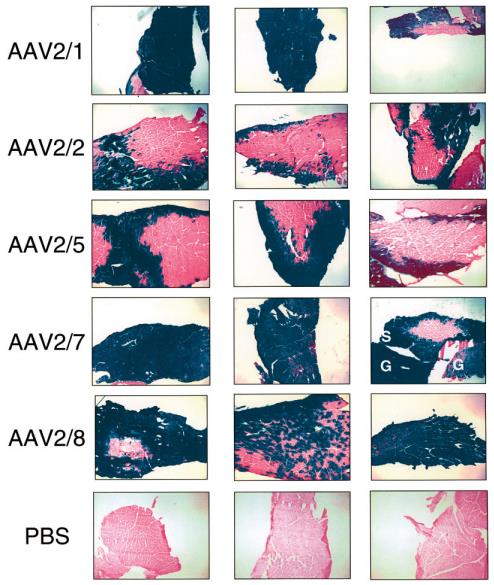
Transduction of muscle fibersby different AAV serotypes.
J Gene Med 2005; 7: 442–451.
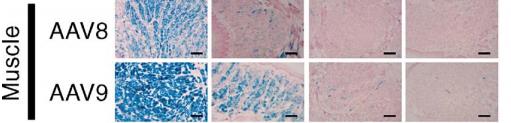
Representative photomicrographs of sections of skeletal muscle
MOLECULAR THERAPY Vol. 14, No. 1, July 2006
Eight, intestine
The commonly used serotypes of intestinal tissue are AAV1, AAV2 and AAV5. Common injection methods include oral, enema, intraperitoneal injection, and mesenteric artery injection. Generally, the injection titer is 1×10^11 GC/ml, diluted to 100 μl (diluted with PBS or diluted solution), and can be detected after 2 weeks of injection.
references:
Weinberg, MS, RJ Samulski, and TJ McCown, Adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy for neurological disease. Neuropharmacology, 2013. 69: p. 82-8.
Iwata, N., et al., Global brain delivery of neprilysin gene by intravascular administration of AAV vector in mice. Sci Rep, 2013. 3: p. 1472.
Pang, JJ, et al., Comparative analysis of in vivo and in vitro AAV vector transduction in the neonatal mouse retina: effects of serotype and site of administration. Vision Res, 2008. 48(3): p. 377-85.
Lisowski, L., et al., Selection and evaluation of clinically relevant AAV variants in a xenograft liver model. Nature, 2014. 506(7488): p. 382-6.
Wang, L., et al., Sustained expression of therapeutic level of factor IX in hemophilia B dogs by AAV-mediated gene therapy in liver. Mol Ther, 2000. 1(2): p. 154-8.
Nathwani, AC, et al., Safe and efficient transduction of the liver after peripheral vein infusion of self-complementary AAV vector results in stable therapeutic expression of human FIX in nonhuman primates. Blood, 2007. 109(4): p. 1414- twenty one.
Manno, CS, et al., Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat Med, 2006. 12(3): p. 342-7.
Palomeque, J., et al., Efficiency of eight different AAV serotypes in transducing rat myocardium in vivo. Gene therapy, 2007. 14(13): p. 989-997.
Vassalli, G., et al., Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors achieve prolonged transgene expression in mouse myocardium and arteries in vivo: a comparative study with adenovirus vectors. International Journal of Cardiology, 2003. 90(2-3): p. 229-238.
Bish, LT, et al., Adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 9 provides global cardiac gene transfer superior to AAV1, AAV6, AAV7, and AAV8 in the mouse and rat. Human gene therapy, 2008. 19(12): p . 1359-1368.
Halbert, CL, et al., Repeat transduction in the mouse lung by using adeno-associated virus vectors with different serotypes. Journal of virology, 2000. 74(3): p. 1524-1532.
Takeda, S., et al., Successful gene transfer using adeno-associated virus vectors into the kidney: comparison among adeno-associated virus serotype 1-5 vectors in vitro and in vivo. Nephron Exp Nephrol, 2004. 96(4): p. e119-26.
Qi, YF, et al., Comparison of the transduction efficiency of tyrosine-mutant adeno-associated virus serotype vectors in kidney. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2013. 40(1): p. 53-5.
The potent dial of adeno-assoc iated viral vectors for gene delivery to muscle tissue. Expert Opin Drug Deliv., 2014. 11(3).
Z Wang1, H.-IM, 3, J Li1, L Sun1, J Zhang1 and X Xiao1,2, Rapid and highly efficient transduction by doublestranded adeno-associated virus vectors in vitro and in vivo. Gene Therapy, 2003. 2003(10 ): p. 2105-2111.
Polyak, Steven, et al. Gene delivery to intestinal epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo with recombinant adeno-associated virus types 1, 2 and 5. Digestive diseases and sciences 53.5 (2008): 1261-1270.
Polyak, S., et al., Gene delivery to intestinal epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo with recombinant adeno-associated virus types 1, 2 and 5. Digestive diseases and sciences, 2008. 53(5): p. 1261-1270 .
YT-M95
YT-M95
Shenzhen Sunshine Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.yatwinsz.com