Accelerated Solvent Extraction - Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in PM2.5 by Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry
Li Chunli
Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd.
Key words
Haze; polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, ASE350; TSQ 8000 triple quadrupole GC/MS; HJ646-2013
introduction
With the development of industry, environmental problems have been severely challenged. For example, in 2013, many places in China suffered from severe haze. At present, inhalable particulate matter (PM2.5, particles with a particle size below 2.5 microns) has become a key project in environmental monitoring. According to reports in the literature, PM2.5 can cause respiratory damage, which is directly related to respiratory diseases, lung diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and even toxicity such as immunotoxicity, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicity [1]. According to WHO estimates, more than 2 million people died in 2011 due to inhalation of fine particles from indoor and outdoor air pollution.
PM2.5 is a very complex mixture of carbon particles, inorganic salts and their acid radicals, metals, organic compounds and pathogenic microorganisms. Among the organic compounds carried by PM2.5, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are the most harmful, and they have strong mutagenic, carcinogenic and teratogenic effects, and are bioaccumulative and persistent. According to China's Ambient Air Quality Standard (GB 3095-2012), the daily average limit of benzo(a)pyrene is 0.0025 μg/m3 [2]. For the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, a number of detection standards for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in particulate matter in ambient air have been released worldwide. In 2013, China also issued a new standard HJ646-2013 "Environmental air and exhaust gas in the gas phase and particulate matter. Determination of Cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons - Mass Spectrometry. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are biphenyl compounds in which a hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom is replaced by chlorine. It has 209 isomers and homologues and is one of environmental persistent organic pollutants. Listed as one of the 12 categories of POPs that are prioritized in the Stockholm Convention. PCBs are important endocrine disruptors, teratogenic, carcinogenic and mutagenic, and are important organic pollutants that endanger human health. Unlike conventional organic pollutants, such POPs are extremely difficult to degrade in the natural environment and can be transported through carriers such as water or air, resulting in global spread of pollution.
In the standard HJ646-2013, the pretreatment uses Soxhlet extraction, and each sample has an extraction time of 16 hours, which takes a long time and is costly. The pretreatment method adopted in this experiment, Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE), has faster extraction speed and efficiency than conventional Soxhlet extraction and less solvent. The technology extracts target components in solid or semi-solid samples with solvents at higher temperatures (40 °C–200 °C) and high pressures (1500 psi). ASE has the advantages of high extraction efficiency, fast speed and low solvent usage. [3]. At present, ASE is widely used in the fields of environment, food, and medicine. The EPA 3545A method is a pretreatment method that uses ASE to extract multiple organic contaminants from environmental samples [4]. This method refers to the HJ646-2013 standard and uses accelerated solvent extraction-series gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in PM2.5. The method is simple and rapid, and the complex matrix is ​​sufficiently reduced by secondary mass spectrometry scanning. The influence of background interference in the sample improves the detection sensitivity of the target compound. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, good stability, and wide linear range.
Experimental part
1.1 Instruments and reagents
Mass Spectrometry Instruments: TSQ 8000 Mass Spectrometer (Thermo ScientificTM, USA); Gas Chromatograph: Trace 1310 GC with AI l310 Autosampler (Thermo ScientificTM, USA);
Column: TG-5MS 30 m*0.25 mm*0.25 μm capillary column; Thermo ScientificTM DionexTM ASETM 350 accelerated solvent extraction with 10 mL stainless steel extraction cell (P/N 068087), 60 mL collection bottle (P/N 048784) Thermo ScientificTM Reacti-Therm Nitrogen Blowing Apparatus (PN: 1003290002-00) Reagents: n-Hexane: Pesticide Level;
Thermo ScientificTM Diatomaceous Earth (1 kg) (P/N 062819)
Thermo ScientificTM Cellulose Membrane (27 mm) (P/N 068093)
1.2 Instrument method
Gas phase method:
Column oven: 70 °C for 1 min, 25oC/min to 140 oC, then increase to 240 oC at 10 oC/min, and finally heat up to 300 °C at 5 °C /min for 3 min; inlet: Splitless injection, no split time: 1 min, liner: inert without split (item number: 453A1925), inlet temperature 270 oC; carrier gas: constant flow, 1 ml/min; transmission line: 280 oC
Mass spectrometry method:
The ion source temperature is 300 oC, using the Acquisition-Timed method, SRM scanning, and the specific detection ion pair is shown in Table 1:
Table 1. Mass spectrometry conditions for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls
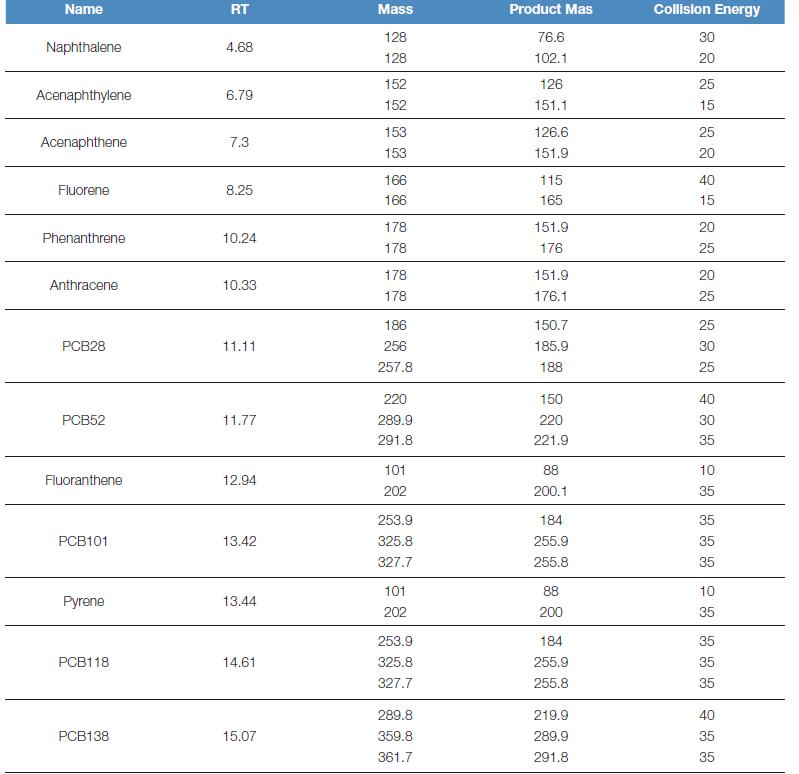
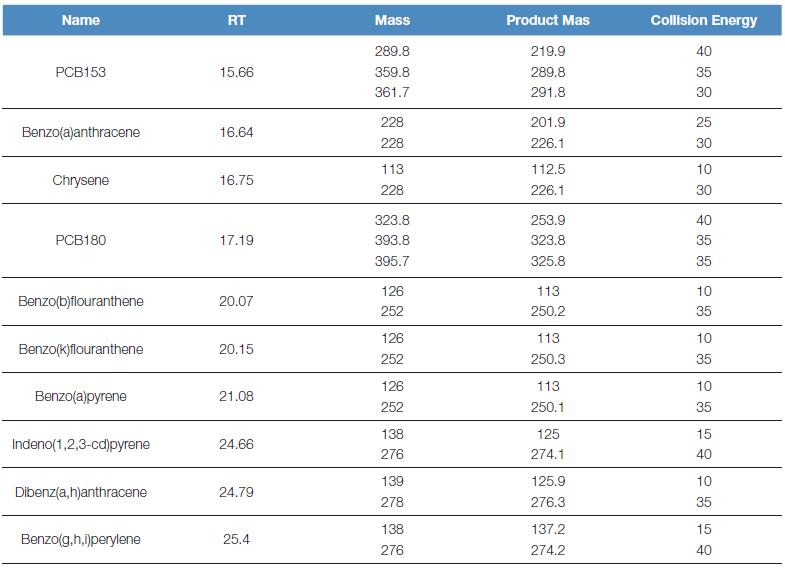
1.3 sample collection
Reference Standard HJ646-2013: PM2.5 particles were collected using MTL's quartz membrane with a sampling flow of 100 L/min and a sampling time of 24 h. After the sample is collected, protect it from light below 4 °C.
1.4 sample preparation
Take a sample quartz filter, carefully roll it into a loop with a tweezers, place it in an extraction cell (10 mL) with a cellulose membrane on the bottom layer, add an appropriate amount of diatomaceous earth, and extract according to the following accelerated solvent extraction conditions. After the extraction, the extract was concentrated by nitrogen to near dryness, and the volume was adjusted to 1 mL by adding n-hexane, and analyzed by direct GC-MS/MS.
2. Analysis of experimental results
2.1 Chromatographic separation results
We can determine the SRM mass spectrometry condition (parent ion-subion-collision energy) of each compound by optimizing the collision energy by Auto-Time-SRM mode. See Table 1 under this condition, and the SRM chromatogram of the target can be obtained. 1.
2.2 Minimum detection limit of the method
S/N=3 is used as the detection limit, and S/N=10 is the quantitative limit of the computational noise ratio. The detection limit spectrum is shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the detection limit of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is 0.1 μg/L. It can be seen from Fig. 3 that the detection limit of 7 polychlorinated biphenyls is 0.05 μg/L. The detection limit of this method is better than other reported values, which can ensure the qualitative and quantitative detection of 23 organic pollutant residues in the sample.
2.3 method linearity, detection limit and precision
The mixed standard solutions were prepared at the concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, and 50.0 μg/L, respectively, by the above methods, and the linearity of each component was examined. The results showed that the 23 components on the surface had a good linear relationship between 0.5 and 50.0 μg/L, and the linear correlation coefficients were all greater than 0.991 (see Table 2). The same sample was continuously injected for 7 stitches, and the RSD was between 0.79 and 3.23% with good repeatability. At the same time, the detection limit of each component was calculated by three times the signal-to-noise ratio, and the detection limit of each component was between 0.05 - 0.1 μg/L (see Table 2).

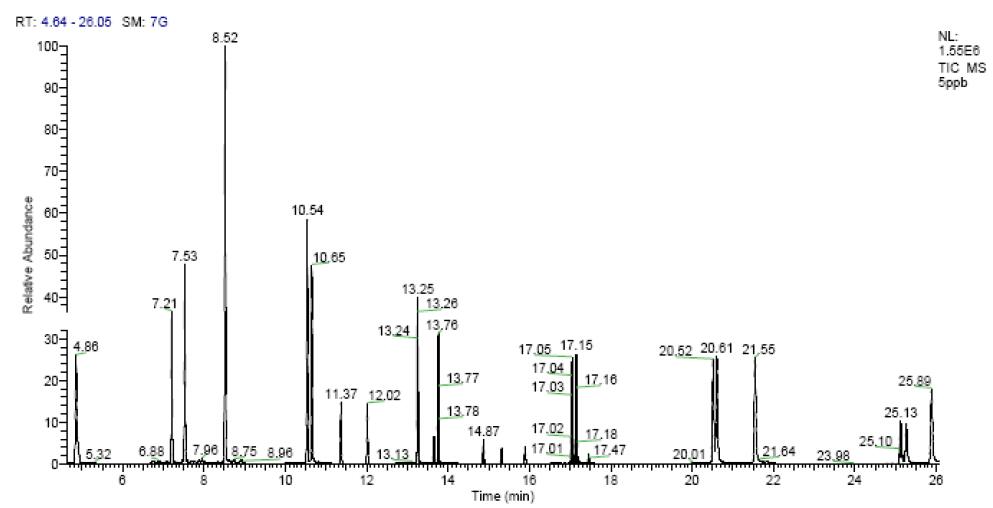
Figure 1. Standard solution chromatogram (5 μg/L)
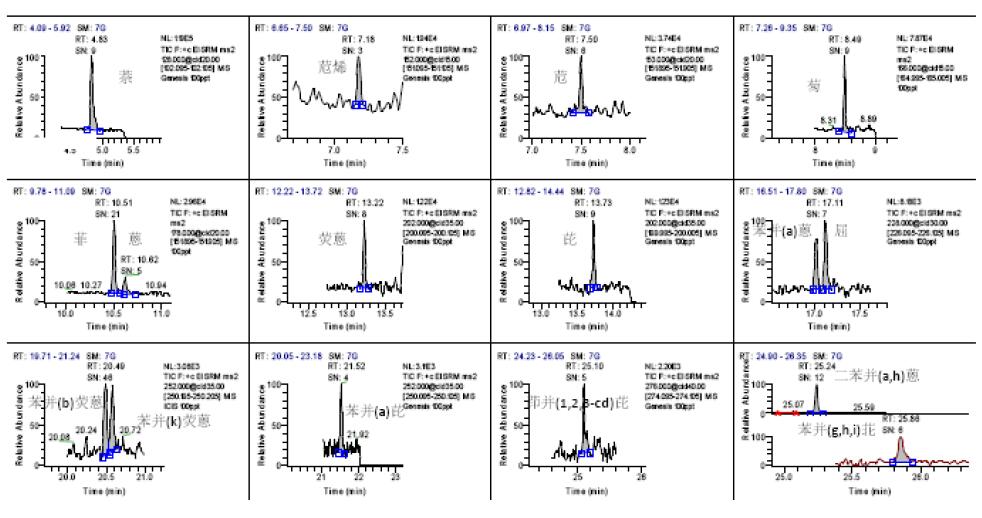
Figure 2. Chromatogram of 0.1 μg/L 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
2.4 blank plus standard recycling
In this experiment, a blank quartz membrane was used for the spiked recovery experiment. The scalar amount was 5.0, 50 ng, and the recovery of the 23 targets was investigated. The experimental results show that the recoveries of the components are between 78.6-119.8%, which meets the requirements of analytical testing (Table 3).
2.5 actual sample determination
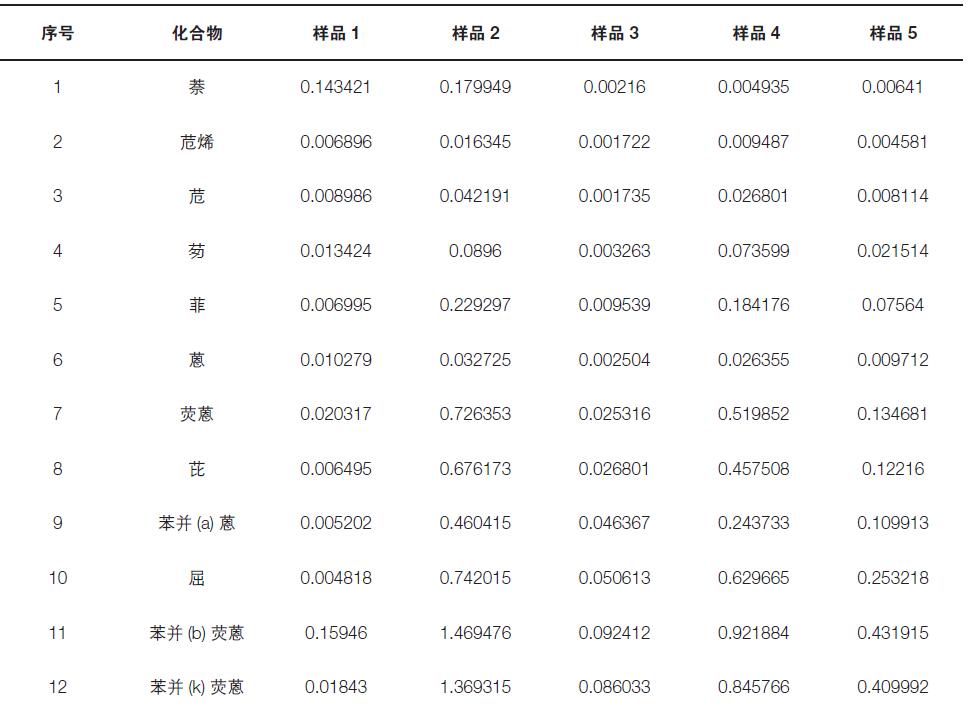
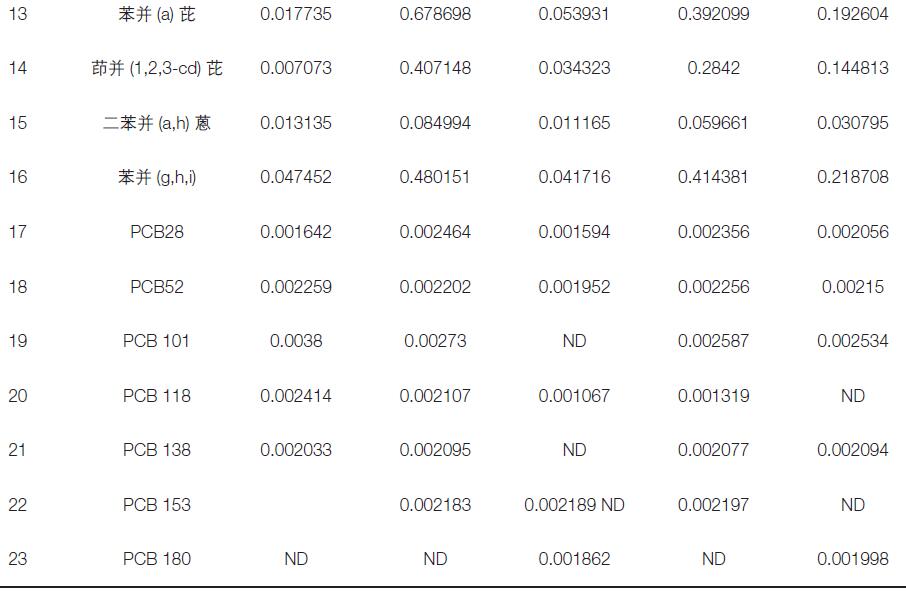
The actual sample of this experiment was provided by the Beijing Environmental Monitoring Station for a total of 5 samples (sample collection rate 100 L/min. Acquisition 24 h). Analyze and test according to the method. The experimental results show that the five samples contain different levels of target organic pollutants (see Table 4).
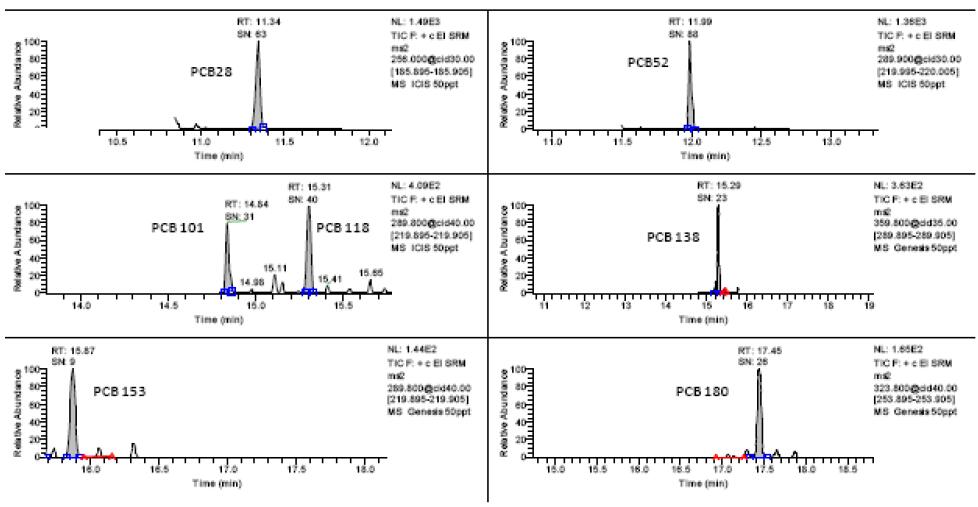
Figure 3. Chromatogram of 0.05 μg/L of 7 polychlorinated biphenyls
Table 2. Retention time, linearity, and RSD% statistics
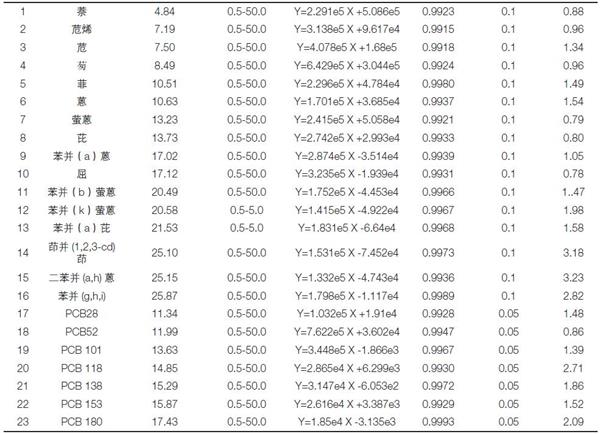
Table 3. Recovery rates of 23 target additions
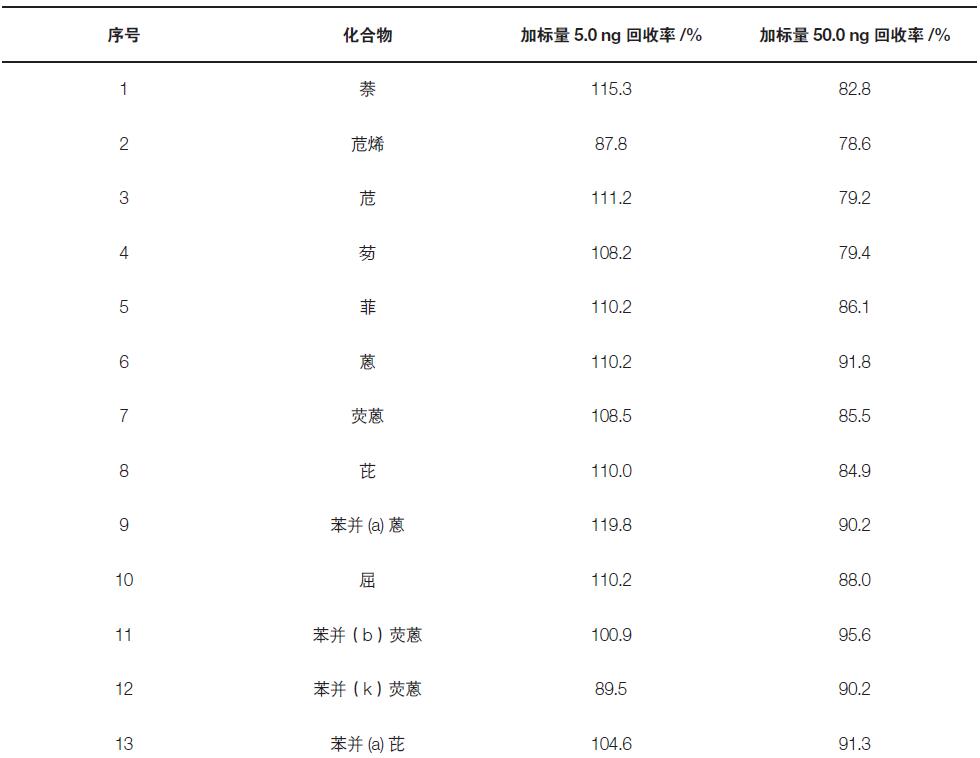
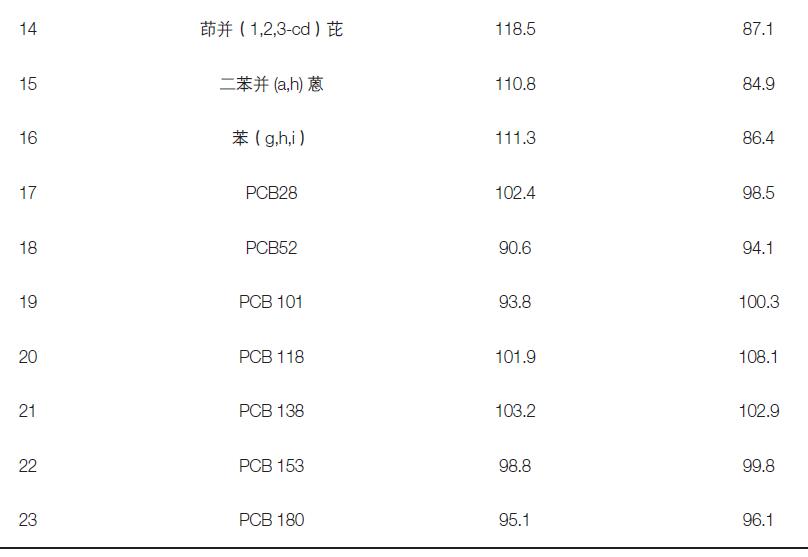
Table 4. 23 target organic pollutants in the sample (in ng/m3)
3. Conclusion
In this paper, the accelerated solvent extraction-triple quadrupole gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (ASE-GC/MS) is used to determine the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5. The sample preparation can be completed in only 20 minutes without complicated manual pretreatment. Compared with traditional Soxhlet extraction, accelerated solvent extraction not only consumes less time, consumes less reagents, but also has simple operation and high recovery. At the same time, TSQ 8000 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer provides ultra-high sensitivity and detection limit for the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls, which can meet the detection requirements of trace amounts of PAHs and PCBs in PM2.5.
references
[1] Yang Xinxing, Feng Lihua, Zhai Peng. Atmospheric particulate matter PM2.5 and its damage[J]. Foreword Science, 2012, 21(6): 22-31.
[2] National Standard of the People's Republic of China, GB 3095-2012 "Environmental Air Quality Standards" [S].
[3] Qi Shifen. Principle and Application of Accelerated Solvent Extraction[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2001, 20(3): 299-300.
[4] EPA Method 3545A. Pressurized Fluid Extraction (PFE) [S].
Related links: PM2.5's overall solution and method package introduction
squid Ring
Squid Ring
ZHEJIANG EVERNEW SEAFOOD CO.,LTD , https://www.evernewseafood.com