Quantum dots, as inorganic synthetic nanomaterials, have unique optical properties beyond traditional fluorescent dyes, such as high fluorescence, no light protection, no quenching, and are a new generation of high-quality fluorescent probes.
In the single-molecule imaging technique, the use of fluorescent probes for single-molecule labeling requires high fluorescence brightness to meet sensitivity and resolution requirements, while requiring long observation time, difficulty in quenching, and long-term excitation of lightfastness. bleach. For the above requirements, quantum dots have an irreplaceable optical advantage.
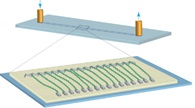
Figure 1 DNA curtain pattern
The portions arranged in parallel in the figure are DNA anchored to a solid phase matrix.
The DNA curtain (Figure 1) is a technique for analyzing the interaction of DNA with proteins in vitro. In this technique, the DNA sequence is anchored to the solid phase matrix, and the protein molecules are fluorescently labeled with quantum dots, so that the binding and action modes of DNA and protein can be dynamically observed and analyzed in real time.
Professor Jennifer A. Doudna of the University of California at Berkeley and Professor Eric C. Greene of Columbia University published a report titled "Exogenous DNA in the E. coli CRISPR-Cas System" in the top biomedical journal CELL in November 2015. Processing research papers. The subject is based on the DNA curtain technology, which anchors the DNA sequence to the solid phase matrix, and uses the quantum dot-labeled Flag antibody to fluorescently label Cascade (Fig. 2), and observes the real-time dynamic observation of green DNA and magenta Cascade. To analyze the interaction patterns of the two, help to elucidate the mechanism of action of the bacterial CRISPR system to foreign DNA.
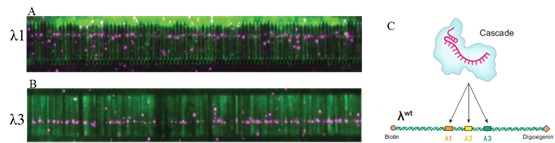
Figure 2 E. coli Cascade targeted binding mode
A. Wide field total internal fluorescence microscopy (TIRF) imaging shows that the quantum dot-labeled Cascade (magenta) binds to the DNA (green) lambda sequence.
B. TIRF imaging shows that Cascade binds to the λ3 sequence of DNA.
CE coli Cascade maps to different binding sites by crRNA.
Source: Redding S, Sternberg SH, Marshall M, Gibb B, Bhat P, Guegler CK, Wiedenheft B, Doudna JA, Greene EC. Surveillance and Processing of Foreign DNA by the Escherichia coli CRISPR-Cas System. Cell 2015;163( 4): 854-65
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
picc catheter line,picc line,Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter,1.9 fr picc line catheter
Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.jssinoanesthesia.com