Liposomes can be used as human drug delivery vehicles, and immunoliposomes (ILs) are conjugated to antibody-loaded liposomes, and released by contact by binding of antibodies to target cell surface antigens or receptors. , adsorption, phagocytosis, swallowing and fusion, release the encapsulated drugs, specifically killing target cells, thus completing targeted drug delivery and specific treatment. Anti-cancer drugs can be targeted for delivery to tumor cells against immunoliposomes of HER2 and EGFR, and have been used in clinical tumor therapy tests. In the development of immunoliposome drug delivery systems, liposomes need to be traced at the cellular and subcellular levels to monitor the temporal and spatial characteristics of tumor cells. Quantum dots (QDs), as nano-fluorescent probes, have ultra-high brightness and excellent light stability, making them a good choice for developing multi-functional drug-loading systems that can be optically traced.
John W. Park, University of California, linked the HER2 antibody scFv fragment to liposomes and coupled quantum dots to obtain traceable, anti-tumor drug (Doxorubicin) immunoliposomes (QD-conjugated immunoliposome- Based on nanoparticles, QD-ILs) (Figure 1). In in vitro cytology experiments, the above-mentioned quantum dot-labeled immunoliposomes are efficiently taken up by breast cancer cells with high expression of HER2 by laser confocal microscopy and flow cytometry observation, and each HER2 positive cell passes immune lipids. The number of quantum dots taken up by the plastid reached ~2.2×10 6 , and no cytotoxicity was found. In nude mice, immunoliposomes significantly prolonged the residence time of quantum dots in the blood circulation, with a plasma terminal half-life of 2.9 h and a free quantum dot with a half-life of less than 10 min. The HER2 overexpressing cell MCF-7/HER2 was used to construct an animal model of breast cancer. The quantum dot-labeled immunoliposomes were injected through the tail vein. The fluorescence imaging showed that QD-ILs localized to the tumor site and had significant antitumor activity. Figure 2); At the same time, a three-month toxicity test was performed, and nude mice showed no weight loss and other significant toxicity. In conclusion, the combination of quantum dots and immunoliposomes in drug-loaded systems provides novel and intuitive research tools for in vitro and in vivo targeted drug research.
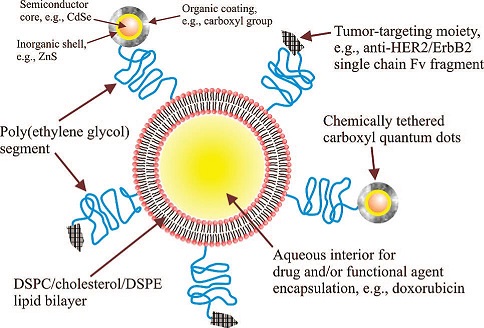
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of quantum dot-labeled immunoliposome drug delivery system (QD-ILs)
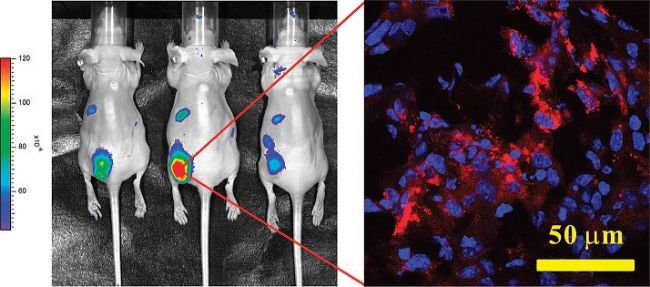
Figure 2 In vivo fluorescence imaging of a quantum dot-labeled immunoliposome drug delivery system
Source of the document:
Squid Rings Raw,Frozen squid rings,This year's Squid Rings
ZHOUSHAN GENHO FOOD CO.,LTD , https://www.genho-food.com